The Shared Responsibility of Cloud Security
Over the years, we have seen a rise in both attack frequency and diversity of malicious software used. With increases in cloud incidents related to vulnerability scanning, web application attacks and brute force attacks, it is crucial for you to understand the types of threats potentially targeting you on the cloud so you can build a security-in-depth strategy to defend your environment from malicious attacks.
In Alert Logic’s Annual Cloud Security Report 2014, web application attacks, brute force attacks and vulnerability scans were the most pronounced attacks experienced in the Cloud Hosting Provider environments, each impacting over 40% of the cloud hosting base. Brute force attacks have surged, likely due to the increasing presence of “theft worthy” data in the cloud, with vulnerability scans typically coupled with brute force attacks in terms of attack style and process.

Real-time analysis across 2200 customers with 232,364 incidents. Source: Alert Logic Cloud Security Report 2014.
In the cloud, a key to being secure is a solid understanding of the shared security model that exists between you (the customer) and your cloud provider. Without this, you may make assumptions that your cloud provider is protecting you, when in fact you are actually responsible for particular security functions.
Your cloud provider is responsible for securing the foundational services, such as computer power, storage, database and networking services, but you will be responsible for the configuration of those services. At the network layer, your service provider is responsible for network segmentation, perimeter services, some DDOS and spoofing.
But you are responsible for network threat detection, reporting and any incident reporting. At the host layer, you are responsible for access management, patch management configuration hardening, and security monitoring and log analysis. The application security components of your site are 100% your responsibility. The model below shows a breakdown of responsibilities between you and your service provider:
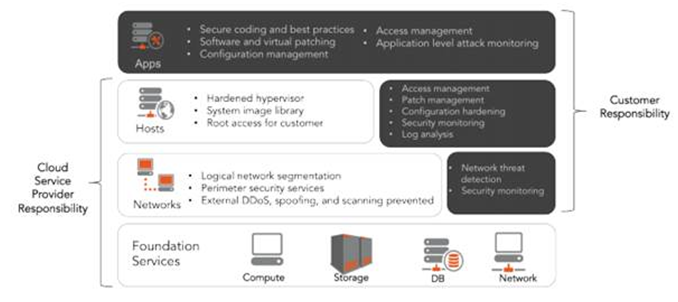
Understanding your role and the role of your cloud provider will not only help you make the best decision concerning your cloud infrastructure, it will also ensure that once implemented your cyber security strategy will efficiently and cost-effectively protect your data from threats to the cloud.
“Cloud services will become ever more critical to business, becoming a cost efficient way to store data, some of which may be sensitive. As a consequence it will also become an attractive target to those seeking to do harm, “says Mark Logsdon, RESILIATM Head of Market Engagement at AXELOS.
“It is vital that we understand how to protect these services and to ensure that that they remain resilient to cyber-attack. This involves everyone across the organisation, at all levels, regardless of role or responsibility. RESILIA, a new cyber resilience best practice portfolio, will help organisations achieve this by highlighting best practice and through providing all users knowledge and confidence to prevent cyber-attacks on an increasingly critical part of the network.”
SEVEN BEST PRACTICES FOR CLOUD SECURITY
There are seven key best practices for cloud security that you should implement in order to protect yourself from the next vulnerability and/or wide scale attack:
1. SECURE YOUR CODE
Securing code is 100% your responsibility, and hackers are continually looking for ways to compromise your applications. Code that has not been thoroughly tested and secure makes it all the more easy for them to do harm. Make sure that security is part of your software development lifecycle: testing your libraries, scanning plugins etc.
2. CREATE AN ACCESS MANAGEMENT POLICY
Logins are the keys to your kingdom and should be treated as such. Make sure you have a solid access management policy in place, especially concerning those who are granted access on a temporary basis. Integration of all applications and cloud environments into your corporate AD or LDAP centralised authentication model will help with this process as will two factor authentication.
3. ADOPT A PATCH MANAGEMENT APPROACH
Unpatched software and systems can lead to major issues; keep your environment secure by outlining a process where you update your systems on a regular basis. Consider developing a checking of important procedures, test all updates to confirm that they do not damage or create vulnerabilities before implementation into your live environment.
4. LOG MANAGEMENT
Log reviews should be an essential component of your organisations security protocols. Logs are now useful for far more than compliance, they become a powerful security tool. You can use log data to monitor for malicious activity and forensic investigation.
5. BUILD A SECURITY TOOLKIT
No single piece of software is going to handle all of your security needs. You have to implement a defense-in-depth strategy that covers all your responsibilities in the stack. Implement IP tables, web application firewalls, antivirus, intrusion detection, encryption and log management.
6. STAY INFORMED
Stay informed of the latest vulnerabilities that may affect you, the internet is a wealth of information. Use it to your advantage, search for the breaches and exploits that are happening in your industry.
7. UNDERSTAND YOUR CLOUD SERVICE PROVIDER SECURITY MODEL
Finally, as discussed get to know your provider and understand where the lines are drawn, and plan accordingly.
Ruaidhri McSharry, SureSkills COO, is leading the Cyber Security programme at SureSkills and is focused on ensuring that people and organisations understand what it is, how it works, why it is critical and demonstrating that without it is like running a business without insurance.
He explains how “RESILIA TM is for organisations and individuals who want to have the knowledge and skills to effectively detect, respond to and recover from cyber –attacks and who need to better understand how effective resilience can enhance the service they provide . The best practice encompasses people, process and technology and provides practical guidance that can be easily adapted and integrated into existing management systems and processes. It enhances existing management strategies and aligns cyber resilience with IT operations, security and incident management.”
Cyber-attacks are going to happen; vulnerabilities and exploits are going to be identified. By having a solid security in depth strategy, coupled with the right training, tools and people that understand how to respond you will ensure your organisation is in a position to minimise your exposure and risk.
To ensure you are properly prepared when a cyber attack happens to you, contact one of our learning consultants today on 01 240 2211 or email info@sureskills.com.
Source: www.alertlogic.com